When buying a computer, you may have come across the term “onboard video card“. But do you really understand what it means? This article will provide you with a clear explanation. Let’s explore the specifications of some popular “onboard video cards” found in computers.
1. 1. Understanding what an “onboard video card” is correctly
1.1. Difference between the concept of GPU and video card
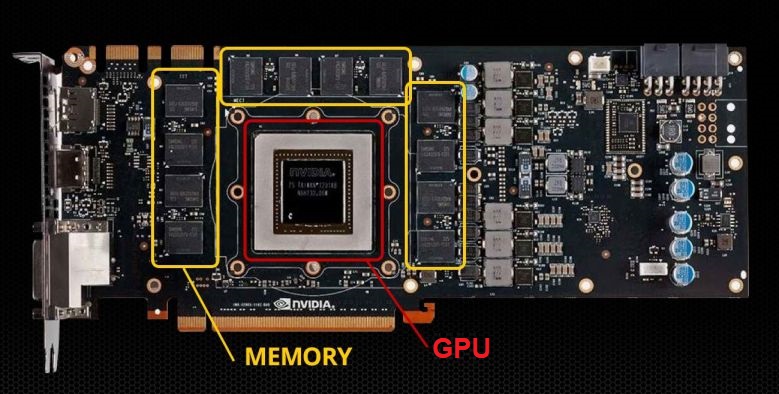
In order to understand the concept of an “onboard graphics card“, it is necessary to have a good understanding of what a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is and what a video card does. A GPU is a chip that processes image data and sends it to the monitor for display. As a result, a computer that lacks a GPU will not be able to display images on the screen.
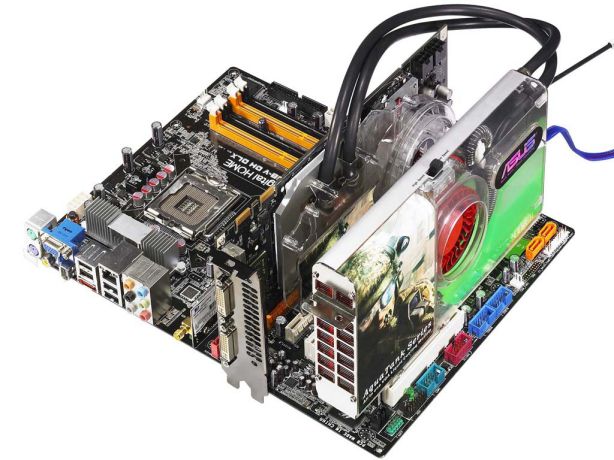
GPUs are sometimes mistaken for “video card” (also known as graphics card). A video card is an electronic device that consists of a GPU, VRAM, cooling system, and semiconductor circuits, which may have connection ports.
1.2. What is the onboard video card?
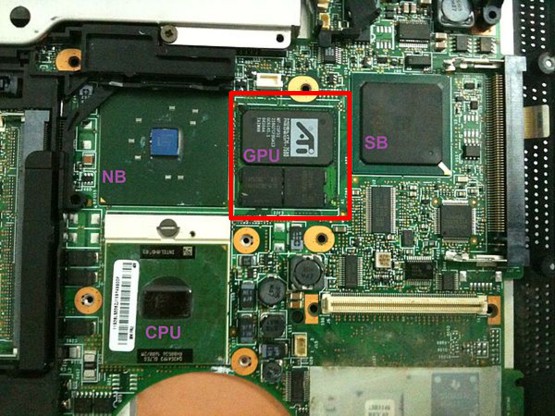
With older generations of desktop motherboards, a GPU chip is integrated into the motherboard. This is referred to as an “onboard video card“. However, “onboard video cards” often have slower processing speeds. This led to the development of powerful dedicated graphics cards, usually attached to the motherboard via PCI or PCIe ports. Dedicated graphics cards are also referred to as discrete cards.
Intel Corporation previously had a solution to integrate the GPU into the NorthBridge chipset. However, they later integrated the GPU into the CPU. Intel refers to this as the iGPU (Integrated Graphics Processing Unit), which is commonly known as the onboard video card. Clearly, it is a misconception, but due to everyday usage habits, we still often refer to iGPU as “onboard video card“.
Laptops use compact components, often relying on integrated graphics processing units (iGPU). However, the graphics processing power of an iGPU is typically not as good as that of a discrete graphics card. A discrete graphics card on a laptop is usually integrated with the GPU, VRAM, cooling system, and semiconductor circuits.
To summarize, an “onboard video card” refers to a GPU that is integrated into the mainboard. However, this type of video card has not been available for a long time. Instead, the GPU integrated into the North chipset or CPU is referred to as an iGPU (Integrated Graphics Processing Unit). Note that iGPU is not as powerful as dedicated graphic cards, which were created to address this issue.
2. Some of Intel’s “onboard video cards”
Intel’s onboard video cards are referred to as iGPUs (Integrated Graphics Processing Units). The iGPU product lines consist of:
Intel HD Graphics
The iGPU series was first introduced in 2010. Then, Intel Iris Graphics and Intel Iris Pro Graphics are the iGPU series released in 2013. Intel HD Graphics and Intel Iris Graphics do not have their own memory. They will take part of RAM to store image data when processing. And Intel Iris Pro Graphics has embedded eDRAM memory.
In addition, an upgrade of Intel HD Graphics is the Intel UHD Graphics series introduced on Intel’s 8th generation CPUs with the codename Coffee Lake in 2017. Intel UHD Graphics can support displays with 4K resolution.
Intel Iris Plus Graphics
They are integrated with 7th-generation Intel CPUs, Kaby Lake. This iGPU series has higher performance than the Intel HD, Iris, and Iris Pro series.
Intel Iris Xe Graphics
They are integrated with 11th-generation Intel CPUs. This is the most potent “onboard video card” from Intel to date (01/01/2022). Intel Iris Xe Graphics can support monitors with 8K or 4K HDR resolution.
2.1. Which iGPUs are included in each generation of Intel CPUs?
| Generation of Intel CPUs | iGPUs |
| 2nd generation Intel® CPU | HD Intel® 3000, HD Intel® 2000 |
| 3nd generation Intel® CPU | HD Intel® 4000, HD Intel® 2500 |
| 4th generation Intel® CPU | Intel® Iris® Pro 5200, Intel® Iris® 5100, HD Intel® 5000, HD Intel® 4600, HD Intel® 4400, HD Intel® 4200 |
| 5th generation Intel® CPU | Intel® Iris® Pro 6200, Intel® Iris® 6100, HD Intel® 6000, HD Intel® 5500, HD Intel® 5300 |
| 6th generation Intel® CPU | Intel® Iris® Pro 580, Intel® Iris® 550, Intel® Iris® 540, HD Intel® 530, HD Intel® 520, HD Intel® 515, HD Intel® 510 |
| 7th generation Intel® CPU | Intel® Iris® Plus 655, Intel® Iris® Plus 650, Intel® Iris® Plus 640, HD Intel® P630, HD Intel® 630, HD Intel® 620, HD Intel® 615, HD Intel® 610, HD Intel® 505, HD Intel® 500 |
| 8th generation Intel® CPU | Intel® Iris® Plus 645, Intel® UHD 630, UHD Intel® 620, Intel® UHD 617, Intel® UHD 615, Intel® UHD 610, Intel® UHD 605 |
| 9th generation Intel® CPU | UHD Intel® 630, Intel® Iris® 655 |
| 10th generation Intel® CPU | Intel® Iris® Plus, Intel® Core™ UHD dedicated to 10th generation Intel® CPU |
| 11th generation Intel® CPU | Intel® UHD 750, Intel® UHD 730, Intel® Core™ UHD dedicated to 11th generation Intel® CPU, Intel® Iris® Xᵉ |
| 12th generation Intel® CPU | Intel® UHD Graphics 770 |
2.2. Specification of some Intel “onboard video cards”
Intel® HD 3000/4000
| Processor Graphics | Intel® HD 3000 | HD Intel® 4000 |
| Graphics Base Frequency | 650 MHz | 650 MHz |
| Graphics Max Dynamic Frequency | 1.15 GHz | 1.05 GHz |
| Graphics Output | eDP/DP/HDMI/SDVO/CRT | N/A |
| Number of Displays Supported | 2 | 3 |
Intel® HD 5500/6000
| Processor Graphics | HD Intel® 5500 | HD Intel® 6000 |
| Graphics Base Frequency | 300 MHz | 300 MHz |
| Graphics Max Dynamic Frequency | 850 MHz | 950 MHz |
| Graphics Video Max Memory | 16 GB | 16 GB |
| Max Resolution (HDMI) | 2560×1600@60Hz | 2560X1600@60Hz |
| Max Resolution (DP) | 3840×2160@60Hz | 3840×2160@60Hz |
| Graphics Output | eDP/DP/HDMI | eDP/DP/HDMI |
| Number of Displays Supported | 3 | 3 |
Intel® Iris® Pro 6200/6100
| Processor Graphics | Intel® Iris® Pro 6200 | Intel® Iris® 6100 |
| Graphics Base Frequency | 300 MHz | 300 MHz |
| Graphics Max Dynamic Frequency | 1.05 GHz | 1.00 GHz |
| Graphics Video Max Memory | 32 GB | 16 GB |
| Max Resolution (HDMI) | 2560×1600@60Hz | 2560×1600@60Hz |
| Max Resolution (DP) | 3840×2160@60Hz | 3840×2160@60Hz |
| Graphics Output | eDP/DP/HDMI/VGA | eDP/DP/HDMI |
| Number of Displays Supported | 3 | 3 |
Intel® Iris® Plus/ Intel® Iris® Plus 655
| Processor Graphics | Intel® Iris® Plus | Intel® Iris® Plus 655 |
| Graphics Base Frequency | 300 MHz | 300 MHz |
| Graphics Max Dynamic Frequency | 1.05 GHz | 1.15 GHz |
| Graphics Video Max Memory | 32 GB – eRAM 128 MB | N/A |
| Max Resolution (HDMI) | 4096 x 2304@60Hz | 4096×2304@30Hz |
| Max Resolution (DP) | 5120 x 3200@60Hz | 4096×2304@60Hz |
| Max Resolution (eDP) | 5120 x 3200@60Hz | 4096×2304@60Hz |
| 4K Support | Yes, 60Hz | N/A |
| Graphics Output | eDP/DP/HDMI | eDP/DP/HDMI/DVI |
| Number of Displays Supported | 3 | 3 |
Intel® Iris® Xᵉ
| Processor Graphics | Intel® Iris® Xᵉ |
| Graphics Max Dynamic Frequency | 1.30 GHz |
| Max Resolution (HDMI) | 4096×2304@60Hz |
| Max Resolution (DP) | 7680×4320@60Hz |
| Max Resolution (eDP) | 4096×2304@60Hz |
| Graphics Output | eDP 1.4b, MIPI-DSI 2.0, DP 1.4, HDMI 2.0b |
| Number of Displays Supported | 4 |
Note: AMD CPU does not refer to “onboard video cards” as iGPUs. AMD designs a series of 64-bit microprocessors that integrate both CPU and GPU in a single device. AMD refers to them as Accelerated Processing Units (APUs).
Reference: Intel® graphics support, AMD Graphics