1. RAM (Random Access Memory)
RAM, or random access memory, provides fast access speed for reading and writing data into memory cells.
Random Access Memory is a type of memory that stores data temporarily while the computer is running. This data is deleted when the computer is powered off.
RAM consists of memory chips that contain millions of transistors and capacitors. Each memory cell is made up of a transistor and a capacitor that stores either bit 0 or bit 1. To prevent power discharge, capacitors need to be refreshed periodically. If power is lost, the data on the memory chip will be lost as well.
2. Types of RAM
There are two types of RAM:
- SRAM (static random-access memory)
- DRAM (dynamic random-access memory)
SRAM (static RAM)
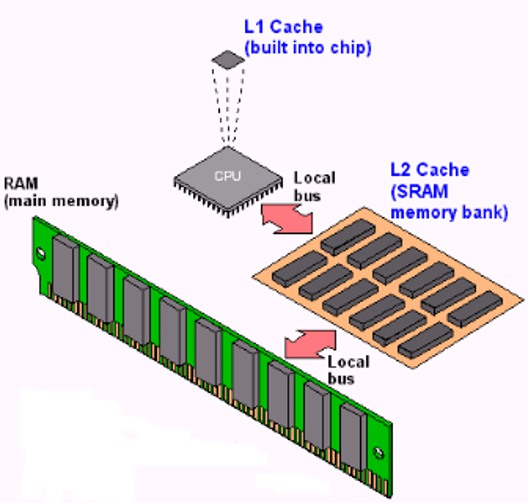
SRAM stands for Static Random Access Memory. It is expensive but has fast access speed. Cache memory is an example of SRAM.
DRAM (dynamic RAM)
DRAM stands for Dynamic Random Access Memory. It uses tiny capacitors to store bits as electric charges and needs to regularly refresh them to maintain valid data. The access speed of DRAM is slower than Static RAM (SRAM).
There are 2 main types of DRAM:
- SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM) is also known as synchronous DRAM. SDRAM includes SDR, DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5.
- RDRAM (Rambus Dynamic RAM) is also known as Rambus. It is commonly used in servers.
Different types of RAM are connected to the mainboard through RAM slots that follow various design standards. References: Types of RAM slots on the motherboard
3. The specifications of RAM
RAM capacity refers to the amount of data that can be stored on a RAM, measured in B/KB/MB/GB.
Bus speed is the operating frequency of RAM or the number of data accesses of RAM in 1 second.
Bandwidth is the amount of data accessed from RAM in 1 second.
For example, a RAM stick with 256 MB DDR – 333MHz – PC2700 (256MB capacity – DDR RAM type – 333MHz bus speed – 2700 MHz bandwidth).