1. What is CPU? Functions of CPU
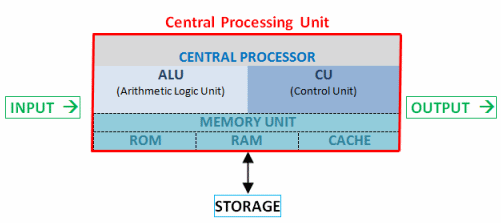
The CPU (Central Processing Unit), also known as the microprocessor or processor, is considered the brain of the computer. It’s a complex integrated circuit that contains millions of transistors.
The computer’s function is to execute the program, which is a sequence of instructions stored in memory. The CPU undertakes this execution, which consists of two steps: reading instructions from memory and executing them. The program execution process is the repetition of reading and executing instructions.
2. History of CPU
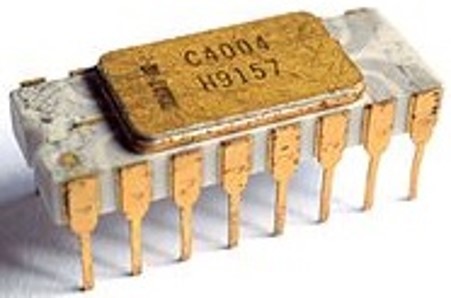
The first commercial CPU was the Intel 4004, introduced by Intel in November 1971. It had 2250 transistors and 16 pins.
The Intel 8080 microprocessor was widely used in the 1970s. It was first introduced in 1974.
In 2006, Intel introduced the Northwood Pentium microprocessor which had 55 million transistors and 478 pins.
In 1971, Intel CPUs had only 2250 transistors. By 2016, they had developed CPUs with 7.2 billion transistors and 22 cores, thanks to the 14 nm process.
Moore’s law is a well-known principle in CPU manufacturing:
The number of transistors per square inch will double every 24 months.
Note: 1 square inch is approximately 6.45 cm².
Once we are unable to reduce the size of a transistor any further, Moore’s law will no longer be applicable.
3. How is CPU classified?
3.1. Classified by CPU’s microarchitecture
Based on microarchitecture, CPUs are classified into:
- Netburst: Willamette, Northwood, Prescott
- P6M/Banias: Banias, Dothan, Dothan533, Yonah
- Core/Penryn: Conroe, Wolfdale, Kentsfield, Yorkfield
- Nehalem (1st generation Core I)
- Sandy Bridge (2nd generation Core I)
- Ivy Bridge (3rd generation Core I)
- Haswell (4th generation Core I)
- Broadwell (5th generation Core I)
- Skylake (6th generation Core I)
- Kaby Lake (7th generation Core I)
- Coffee Lake (8th generation Core I)
- Coffee Lake Refresh (9th generation Core I)
- Ice Lake (10th generation Core I)
- Rocket Lake (11th generation Core I)
- Alder Lake (12th generation Core I)
3.2. Classified by manufacturing process of CPU
It is mainly based on transistor scaling. They are methods of reducing the size of each transistor in the CPU. There are various CPU manufacturing processes, including 130nm, 90nm, 65nm, 45nm, 32nm, 22nm, 14nm, 7nm, 4nm, etc.
3.3. Classified by the purpose of use
Each CPU is designed for specific purposes:
- CPU for mobiles
- CPUs for desktops
- CPU for workstations, servers
4. 4. How does the CPU Work?
When a computer runs a program, the program’s instructions are loaded into RAM memory. The CPU reads and follows these instructions one by one. As it reads and follows the instructions, the decoder decodes them into control signals.
5. Manufacturers of CPUs
Intel and AMD are the two largest manufacturers of CPUs in the market today.
Intel CPU series
- Intel® Core™, Intel® Pentium®, Intel® Celeron® CPU family for Desktops, Laptops, and Notebooks.
- Intel® Xeon™, Intel® Itanium™ CPU family for servers, and workstations.
AMD CPU series
- Phenom™, Athlon™, and Sempron™ CPU family for Desktop.
- Turion™ 64X2 Dual-Core mobile technology microprocessor family, Athlon 64X2, Mobile AMD Sempron CPU family for Laptop, Notebook.
- Athlon MP, Opteron™ CPU family for servers, and workstations.