You may have heard of different types of memory, such as RAM, ROM, HDD, or USB. Though they all fall under the category of memory, they are classified based on their specific characteristics. Let’s explore this further together.
1. Types of computer memory
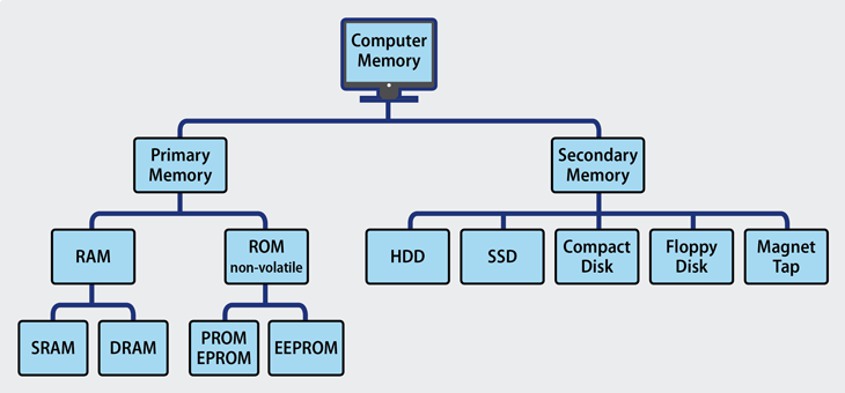
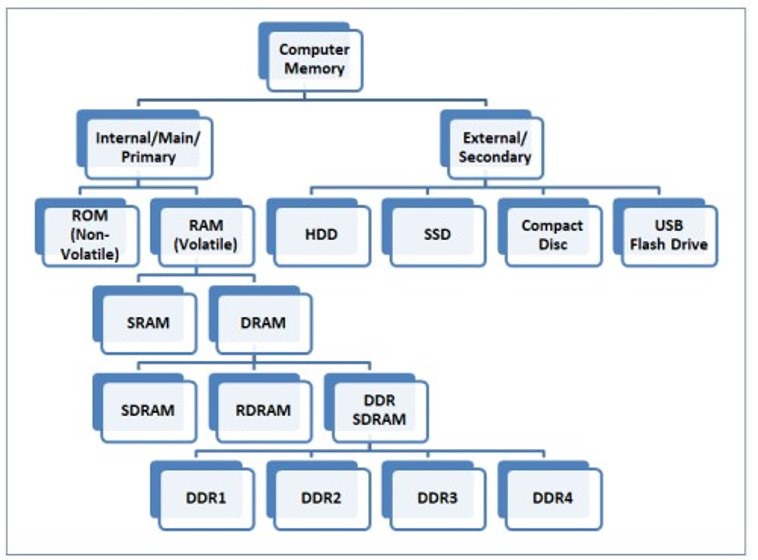
Computer memory can be divided into primary and secondary memory. Primary memory comprises ROM and RAM, while secondary memory includes other storage devices.
This is also known as internal memory, which includes ROM and RAM, and external memory, which refers to other storage devices.
2. ROM memory and types of ROM memory
2.1. ROM memory (Read Only Memory)
ROM is a type of non-volatile memory, which means that any stored data is not lost when the computer is turned off. It is commonly used to store BIOS programs.
The BIOS program stores the specifications of the hardware components, and the manufacturer pre-installs the startup program for the computer.
To recognize a ROM, look for the following characteristics:
- Shape: rectangle or square
- Manufacturer: typically AMI, Phoenix-Award, or Winbond
- Connection type: soldered or mounted to a socket
2.2. Types of ROM memory
PROM (Programmable ROM)
PROM is a chip that can only be programmed once and is read-only. The data on the chip cannot be erased. PROM was created by Wen Tsing Chow in 1956.
EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM)
EPROM data is stored and can be erased with ultraviolet light. It was invented by Dov Frohman in 1971.
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM)
EEPROM-stored data can be erased and rewritten without removal from the computer. The National Research Institute of Japan manufactured EEPROM in 1972.
Flash memory
Fujio Masuoka invented flash memory at Toshiba in 1972. This type of EEPROM has a large capacity and operates on NOR and NAND logic gates at high speed.
Flash memory is also faster than traditional hard drives because it has no moving parts and can access data more quickly. This makes it ideal for use in computers that require high-speed data transfer, such as gaming computers and workstations.
Another advantage of flash memory is its durability. Unlike traditional hard drives, which can be damaged by physical shock or vibration, flash memory is much more resistant to these types of damage. This makes it a more reliable choice for portable devices like laptops and tablets.