A bus is a communication system that transfers data between different components of a computer. There are different types of buses in computers, each with specific characteristics.
1. Types of buses on the mainboard
There are several types of buses, including the System Bus, FSB (Front Side Bus), BSB (Back Side Bus), and Expansion Bus. Each type of bus has a different bus speed. The highest bus speeds are BSB, followed by the System Bus, FSB, and Expansion Bus.
2. System Bus on the mainboard
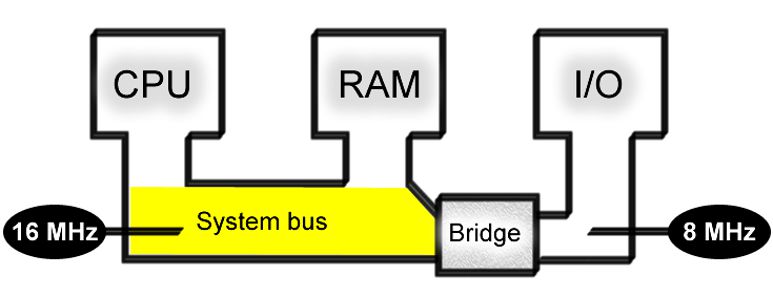
The System Bus is a channel that transfers data between the CPU and memory and I/O devices. The number of data lines (32 or 64 bits) and the clock speed of the mainboard determine the capabilities of this bus.
The System Bus is composed of two parts:
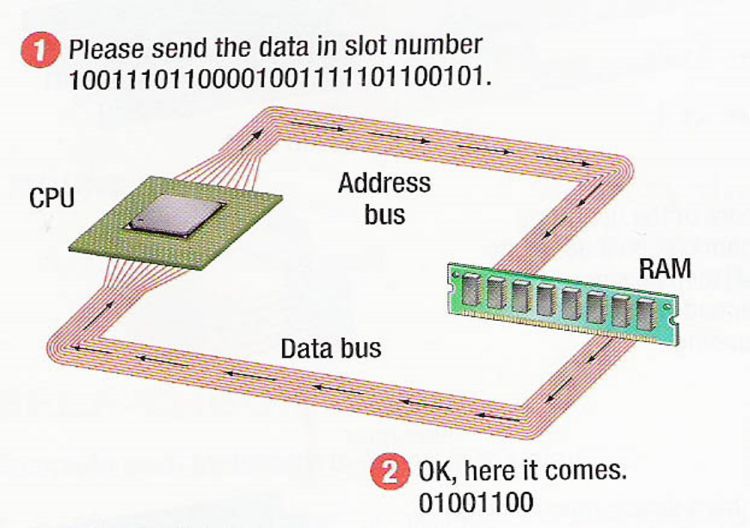
- The address bus transmits the memory cell address to the memory.
- The data bus sends the data from the memory when the memory cell address is identified.
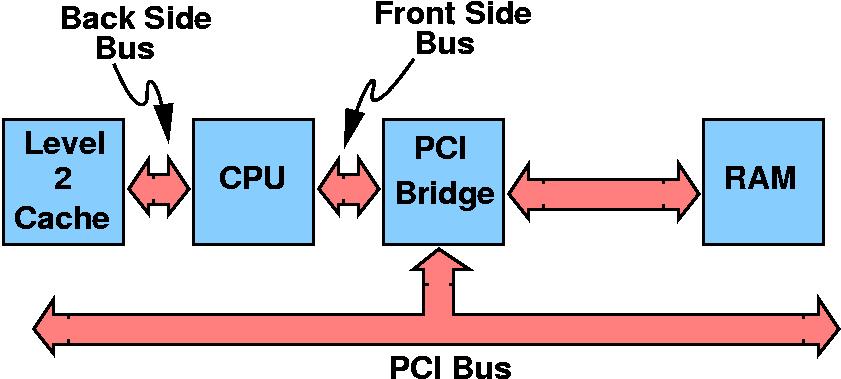
3. FSB (Front Side Bus) và BSB (Back Side Bus)
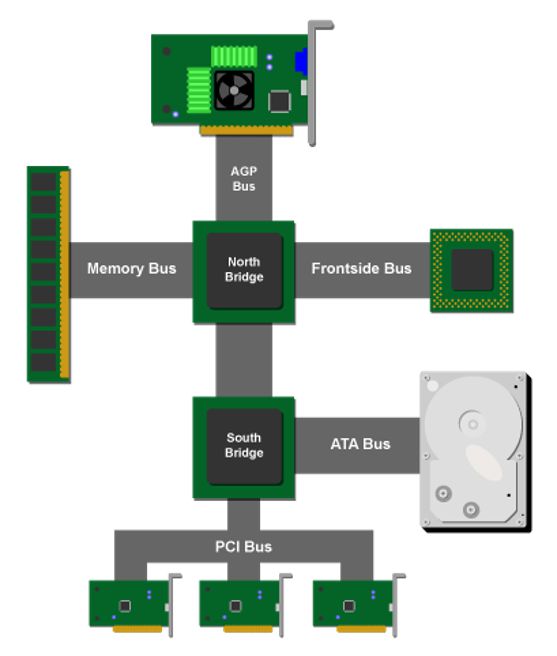
FSB is a data transmission line that connects the chipset and processor. BSB, on the other hand, is a data transmission line that connects the processor and cache memory. It is the highest-speed bus on the mainboard.
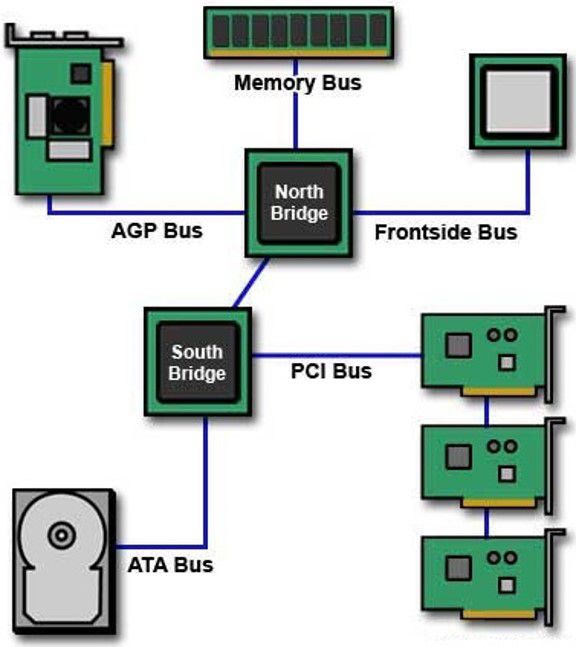
4. Expansion bus on the mainboard
Furthermore, there exist numerous other bus lines that manage the transfer of data between peripheral devices, expansion cards, and chipsets on the mainboard. Some examples include AGP Bus, ATA Bus, and PCI Bus, and together they are known as the Expansion Bus.
An expansion bus allows for the addition of expansion cards to a computer’s motherboard. These expansion cards can provide additional functionality, such as increased graphics processing power, improved audio capabilities, or additional input/output ports.
There are newer types of buses in addition to the expansion buses. These include PCIe and USB. PCIe is for high-bandwidth devices, like graphics cards. USB helps to connect peripheral devices such as keyboards, mice, and external hard drives.