1. Power connector on the motherboard
The power connector on the mainboard is an essential component that connects the power supply unit (PSU) to the motherboard. This connector ensures that the motherboard receives the required power to function correctly. There are several power connectors: the main power connector, the CPU power connector, and the fan power connector.
2. Storage device connectors on the motherboard
The storage devices need to be connected to the motherboard via specific connectors. These are some of the storage device connectors that are usually present on a motherboard:
- FDD (Floppy Disk Drive)
- IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics)
- SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
- SCSI (Small Computer System Interface)
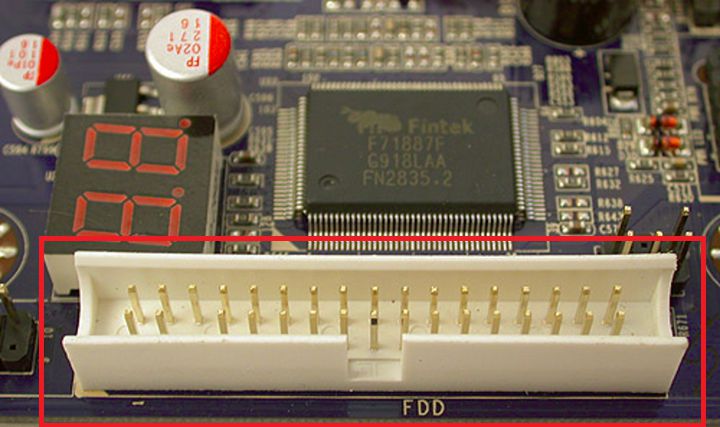
2.1. FDD (Floppy Disk Drive)
The FDD (Floppy Disk Drive) connector standard is a 35-pin connector that is rarely used in modern computing.
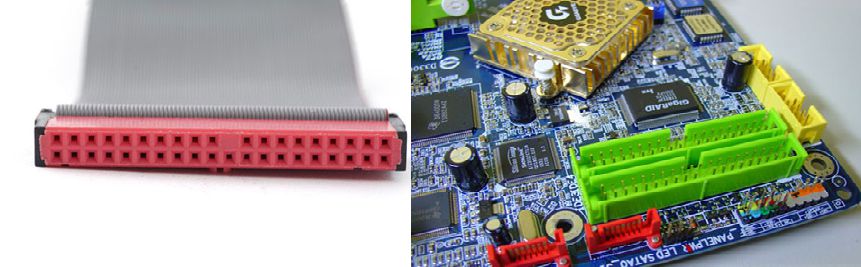
2.2. IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics)
IDE is the standard connector for ATA storage devices. The connectors on an IDE cable consist of 40 pins.
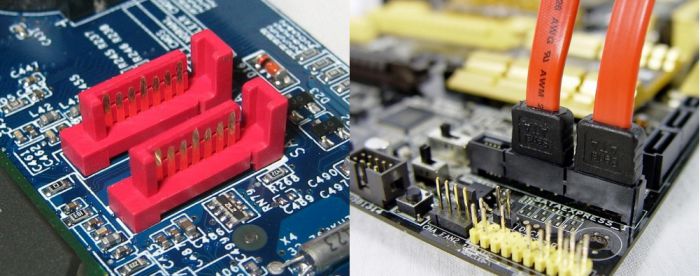
2.3. SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
SATA, or Serial ATA, is a storage device connector standard that was introduced in 2003 to replace the older IDE. This connector standard is capable of achieving transfer rates of up to 6 Gbps, which is significantly faster than the maximum speed of 133 MBps that IDE was capable of achieving.
SATA has data transfer rates of 150MB/s (SATA 1.0), 300MB/s (SATA 2.0), and 600MB/s (SATA 3.0).
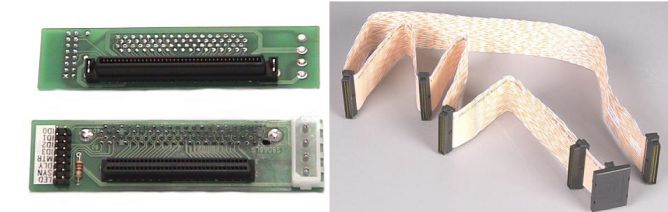
2.4. SCSI (Small Computer System Interface)
SCSI is a standard used in high-end servers, with either 50 or 68 pins. It has a fast data transfer rate of about 320MB/s to 640MB/s.
SCSI also has an error correction system built in to ensure that the transferred data remains accurate. This is important in industries that require the highest level of data integrity. So, SCSI is an excellent choice for businesses that require high-performance data transfer rates and need to ensure that their data remains accurate and reliable.