1. Function of socket on the mainboard
To connect the motherboard and CPU, they must be compatible through a socket. Make sure the socket type matches the processor.
2. Types of sockets
Slot
The CPU is connected to an electronic circuit which is then connected to the mainboard through a slot. Please note that the slot for the CPU is only available on older-generation motherboards.
Socket
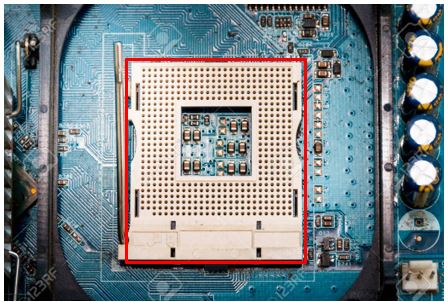
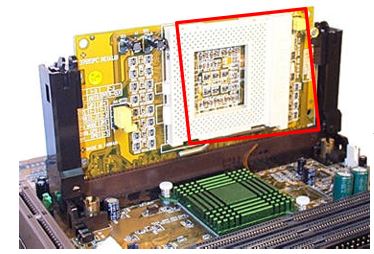
The socket is situated on the mainboard and is responsible for providing a contact point and CPU rack.
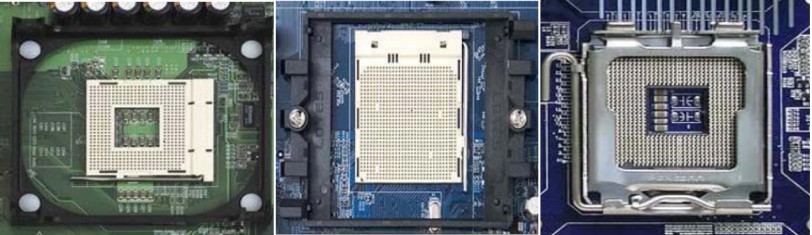
There are various types of sockets:
- Socket 370 is compatible with Intel Pentium III and Celeron CPUs.
- Socket A (462 pins) is compatible with AMD Duron CPUs.
- Socket 423 is compatible with Intel Pentium IV CPUs.
- Socket 478 is compatible with Intel Pentium IV and Celeron CPUs.
- Socket 775 is compatible with Intel Pentium IV and Core 2 Duo CPUs.
- Socket 1156, 1366, 1150, 1151, and 2011 are compatible with Intel Core i3, i5, and i7 CPUs.
- Socket AM2 (939 pins), FM2, and FM2+ are compatible with AMD Athlon 64 CPUs.
Note: The CPU must be compatible with the socket to connect to the socket.
The socket has a cooling fan that cools the CPU.
Moreover, top-of-the-line computers utilized water cooling systems.
In high-performance computers, water cooling systems are often used to cool the CPU. These systems use liquid coolant to more effectively remove heat from the CPU than air cooling systems. Water cooling systems typically consist of a water block that sits on top of the CPU, a pump that circulates the coolant, and a radiator that dissipates the heat. These systems can be more expensive and complex to install than air cooling systems, but they offer improved cooling performance.