1. Functions of Desktop case
The desktop case mounts and protects the computer’s hardware components while enhancing its appearance. The desktop case is also commonly referred to as the PC case.
There are two main types of PC cases:
- Horizontal PC case
- Standing PC case


2. Design standards of Desktop case
PC cases are designed according to the mainboard structure and adhere to AT, ATX, and BTX standards.
– AT (Advance Technology): rarely used today
– ATX (Advance Technology Extended): commonly used
- Full ATX: size 19” x 9.6” (48.26 x 24.4cm)
- Mini ATX: size 11.2”x 8.2” (28.45cm x 20.83cm)
- Extended ATX: size 12”x 13” (30.48cm x 33.02cm)
- MicroATX: size 9.6”x 9.6” (24.4cm x 24.4cm)
– BTX (Balanced Technology Extended): good cooling system
- BTX: size 12.8”x 10.5” (32.512cm x 26.67cm).
- MicroBTX: size 10.4”x 10.5” (26.416 x 26.67cm).
- NanoBTX: size 8.8”x 10.5” (22.352cm x 26.67cm).
- PicoBTX: size 8”x 10.5” (20.32cm x 26.67cm).
Server case: The server case has a different structure, a larger size, and an excellent cooling system, with a complex structure.
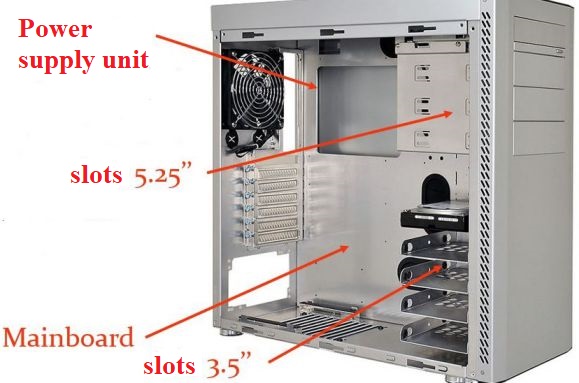
3. Structure of Desktop case
The internal structure of the different case types is very similar. The most commonly used design is still the ATX standard. The ATX case consists of four main components:
- The area for the power supply unit
- The 5.25″ slots, which are usually used for mounting CD and DVD drives
- The 3.5″ slots, which are typically used for mounting HDD and FDD drives
- The area for the mainboard
Front of the case
- Includes power off button, reset button, power signal lights, and hard drive signal.
- It also has an integrated USB port, Audio port, etc.
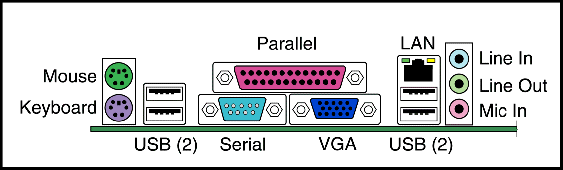
Back of the case
- Includes ports for connecting peripherals.