When purchasing or upgrading a computer, we are typically interested in the specifications of the CPU. This article will introduce in detail the specifications of the CPU.
1. The specifications of the CPU
These are the different specifications for each processor:
- Type of socket
- Processing speed
- Size of register
- Cache memory
- Bus speed
- Instructions Set
- Operating voltage
The processing speed of the CPU
The CPU clock speed is another term for the processing speed of the CPU. It is measured by the number of instruction executions per second, with units of Hz, MHz, and GHz.
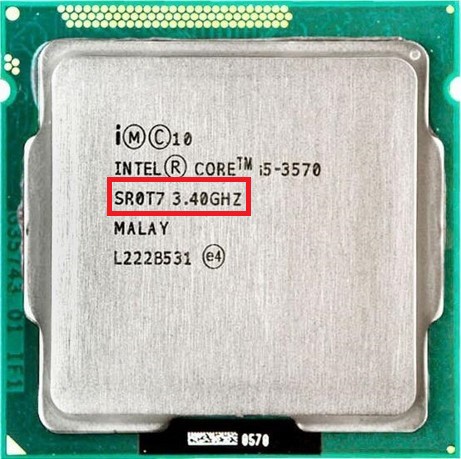
This is an example of an Intel Pentium 4 CPU with a processing speed of 2.8 GHz. And 2.8 GHz = 2,800,000,000 Hz. This means that in one second, the CPU can execute around 2.8 billion instructions.
Size of CPU register
The terms 32-bit and 64-bit CPUs are commonly used to refer to the size of the CPU registers.
With the register in a 32-bit CPU, you can store 232 memory cell addresses, with each cell storing 1 byte of data. This means that a 32-bit CPU can only access up to 4 GB of RAM. Meanwhile, the register in a 64-bit CPU stores 264 memory addresses, which allows a much larger amount of data for the 64-bit CPU to process.
Cache Memory
The cache memory size typically ranges from a few MB, such as 4 MB, 6 MB, 8 MB, to 16 MB.
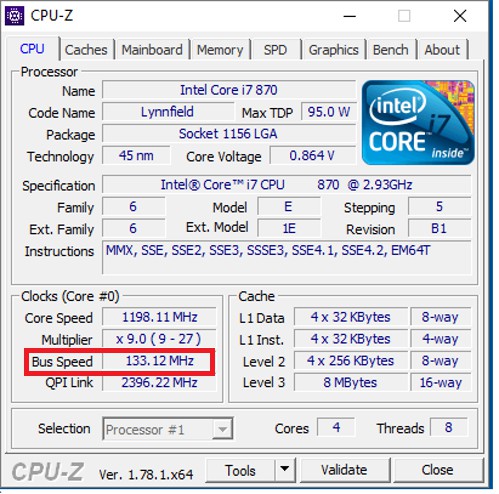
Bus speed
It is the speed in and out between CPU pins, also known as Front Side Bus.
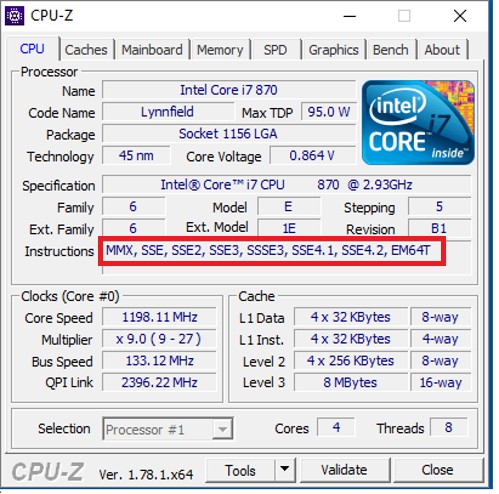
Instruction Set
The instruction set is a series of codes the CPU can interpret and execute. It comprises a sequence of 0s and 1s that control the manipulation and calculation of bits and bytes within the CPU. Standard instruction sets include CISC, RISC, SIMD, MMX, MMX+, SSE, SSE5, and 3Dnow.
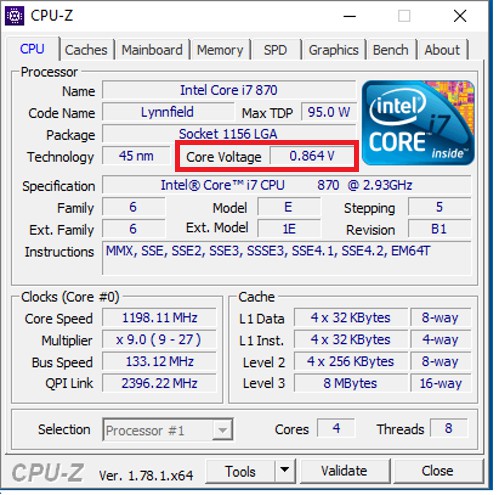
Operating Voltage of CPU
The operating voltage of the CPU refers to the voltage supplied to it. Typically, this voltage has a potential difference of approximately 1.0-1.5V, though power-saving CPU series may have a lower operating voltage.
2. Technologies integrated into the CPU
Hyper-Threading technology
Intel invented Hyper-Threading, a technology that enables running 2 processing threads simultaneously on one processor.
Multi-Core technology
Multi-Core technology enables processors to handle multiple tasks by utilizing several cores that work simultaneously and share the processing workload.
The two commonly used multi-core technologies are Dual Core and Quad Core.
Intel Turbo Boost technology
Intel Turbo Boost is a technology that automatically increases CPU processing speed to match processing requirements. There are two versions of Intel Turbo Boost: 2.0 (released in 2011 with the 2nd generation of Intel Core I – Sandy Bridge) and 3.0 (released in 2016 with the 5th generation of Intel Core I – Broadwell).
Intel HD Graphics technology
Intel HD Graphics is a technology that integrates the graphics chip in Intel’s CPU. It was first introduced in 2010.
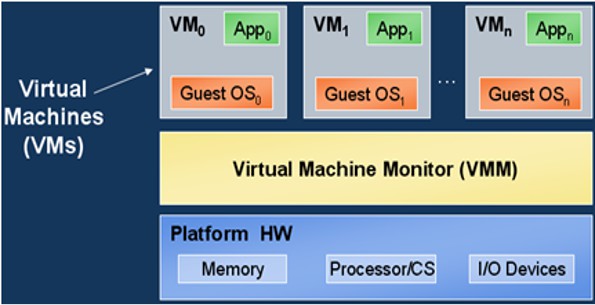
Virtualization technology
Virtualization is the process of creating a virtual version of something at the same level of abstraction, including virtual computer hardware platforms, storage devices, and computer network resources. This is achieved with Intel’s CPUs, called Intel Virtualization Technology (abbreviated as Intel VT or VT-x), and AMD’s CPUs, which are called AMD Virtualization (abbreviated as AMD-V).
Extended Memory 64 Technology (EM64T)
This technology allows for 64-bit computing, which enables the CPU to access large amounts of memory (264 x 8-bit).
There are two forms of CPU support for EM64T technology:
- Compatibility: This allows 64-bit operating systems to run 16-bit or 32-bit applications, with the CPU able to access memory up to 4GB for 32-bit programs, and 1GB for 16-bit programs.
- 64-bit: This allows only 64-bit operating systems and programs to run.