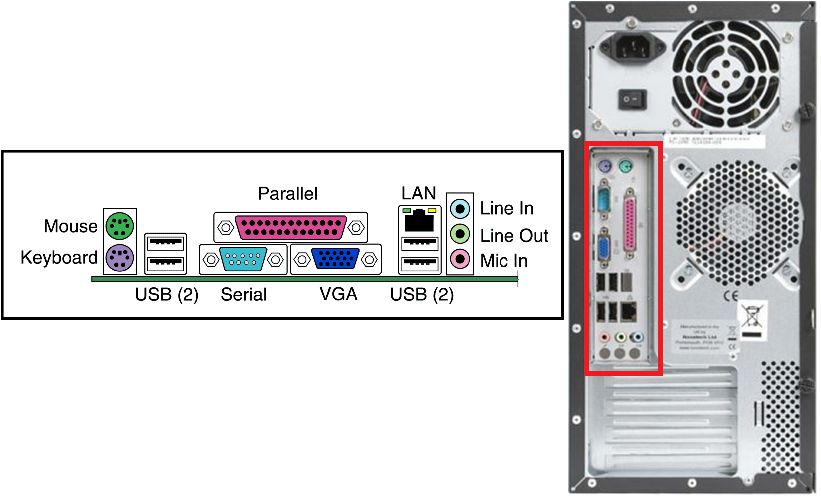
The back panel, also known as the rear panel, is located on the back of the desktop case. It includes many connection ports such as PS/2, Serial, Parallel, USB, DVI, VGA, HDMI, etc. This article will help you learn about all these connection ports.
1. PS/2 port (PlayStation 2)
The PS/2 port on the mainboard helps connect the mouse (green port) and keyboard (purple port). These two ports are not interchangeable and must be properly plugged in. The PS/2 port has 6 pins.
2. Serial port
The serial port is a port that connects peripheral devices such as a keyboard, mouse, and scanner to a computer. It is also referred to as a COM port. It has 9 pins but is rarely used nowadays.
3. Parallel port
The parallel port helps to connect peripheral devices, typically older printers. It has 25 pins and is now rarely used.
4. VGA port (Video Graphics Array)
The VGA port on the mainboard helps connect monitors, projectors, and other similar devices. It is typically blue and has 15 pins.
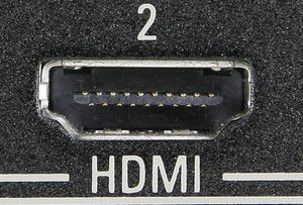
5. HDMI port (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
The HDMI port connects to projectors and has a higher resolution than the VGA port. HDMI ports are typically black and have 19 pins.
6. DVI port (Digital Video Interface)
The DVI port transmits video signals to the monitor. It is typically white and has 24 pins, including 5 analog pins.
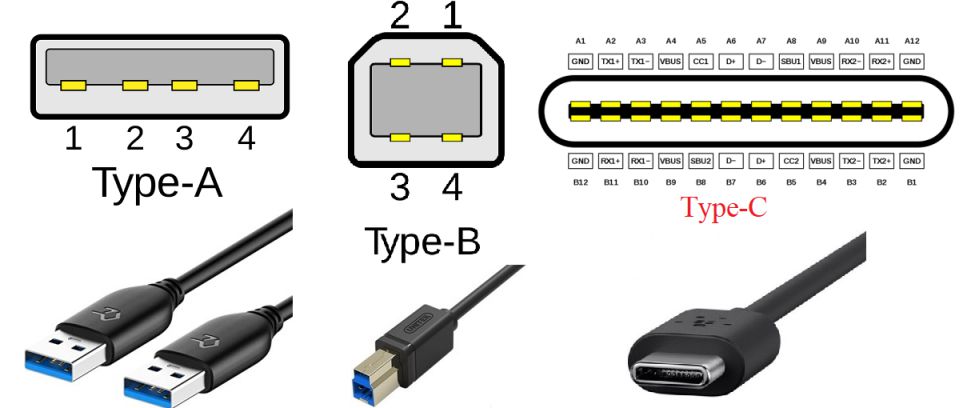
7. USB port (Universal Serial Bus)
USB is a standard for connecting peripheral devices to computers. It has been through four generations: USB 1.x, USB 2.0, USB 3.x, and USB 4.0. USB 2.0 ports are typically colored black, while USB 3.x ports are typically colored blue. There are several types of USB connectors, including USB Type-A, Type-A SuperSpeed, Type-B, Type-B SuperSpeed, and Type-C.
8. RJ45 port (Registered Jack-45)
The RJ45 helps transmit network signals on computers. It has 8 pins.
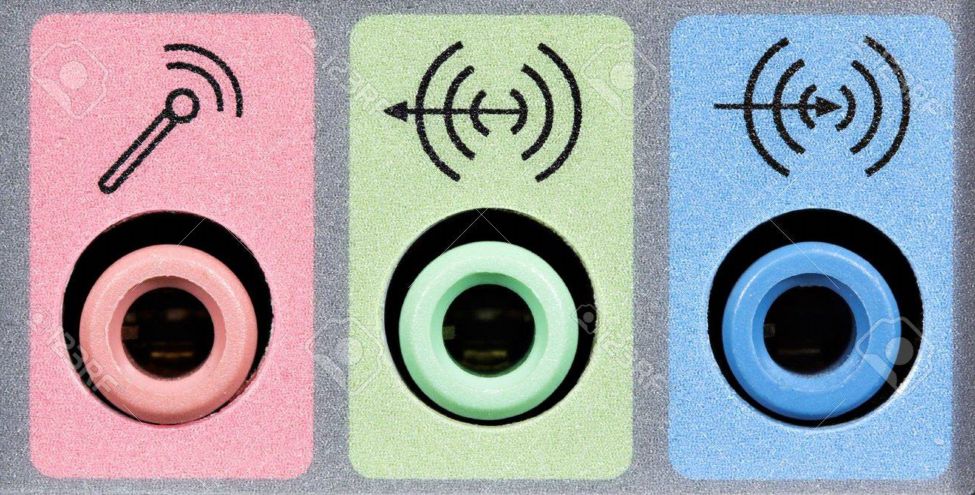
9. Audio port
The audio helps connect to equipment that collects and processes audio signals.
- Pink port: connect to a microphone.
- Green port (Line out): output the signal to an amplifying device such as a speaker.
- Blue port (Line in): receives signals to the computer for processing.