1. Lesson objectives
- Review disassembling and rebuilding Desktop
- Recognizing and reading basic specifications of Desktop mainboard components
2. Instruments preparation
Each student prepares the following tools:
Main tools:
- 01 Desktop computer
- 01 screwdriver
- 01 screw box
Support tools:
- 01 computer cleaning brush
- 01 cleaning cloth
3. Components of the motherboard
3.1. Ports, slots, and ROM BIOS
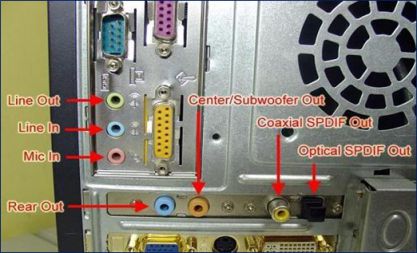
Speaker port, micro port
– These are ports that connect the speaker and microphone to the mainboard.
– Specifications:
- Number of ports
- Color
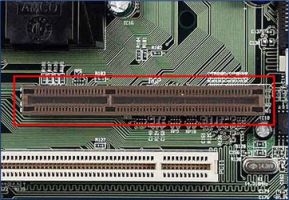
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slot
– PCI is a slot to connect to expansion devices.
– Specifications:
- Color
- Number of ports
- Number of pins
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) slot
– The AGP slot was reserved for graphic cards in older computers.
– Specifications:
- Color
- Number of ports
- Number of pins
ROM BIOS
ROM BIOS is an IC that stores the BIOS program. Its main functions are to start the computer, provide the default version of CMOS SETUP, test the video card and RAM, and manage components on the mainboard (such as the chipset, SIO IC, onboard video card, and keyboard).
– Specifications:
- ROM BIOS model
- Number of pins
3.2. Some other components
Quartz crystal
– Quartz crystal is used to create oscillations and the oscillation frequency is recorded on the back of the quartz crystal.
– Specifications:
- Clock frequency
- Location (near IC, chipset, etc.)
Coil
– Coil is another name for the inductor. Inductors maintain stable currents for power circuits. They are labeled as L or PL on the motherboard.
– Specifications:
- Shape
- Number of coils in the inductor
- Symbol
Capacitor
– A capacitor is an electronic component used for filtering power, filtering noise, and used for oscillator circuits. There are 2 types of capacitors on a Desktop mainboard, including non-polarized ceramic capacitors and polarized electrolytic capacitors.
– Specifications:
- Shape
- Color
- Symbol
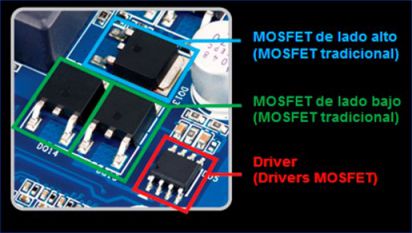
Mosfet (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor)
– Mosfet is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), which is commonly used in digital and analog circuits.
– Specifications:
- Number of pins
- Color
- Number of MOSFETs on the mainboard
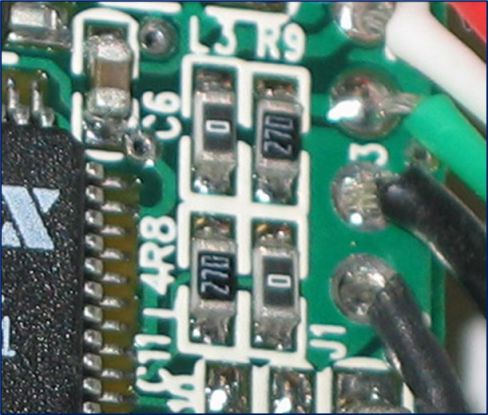
Resistor
– A resistor is a passive component used for the resistance to electric current. The letter R or PR is often used to represent a resistor.
– Specifications:
- Color
- Impedance
- Location (near IC, capacitor, etc.)
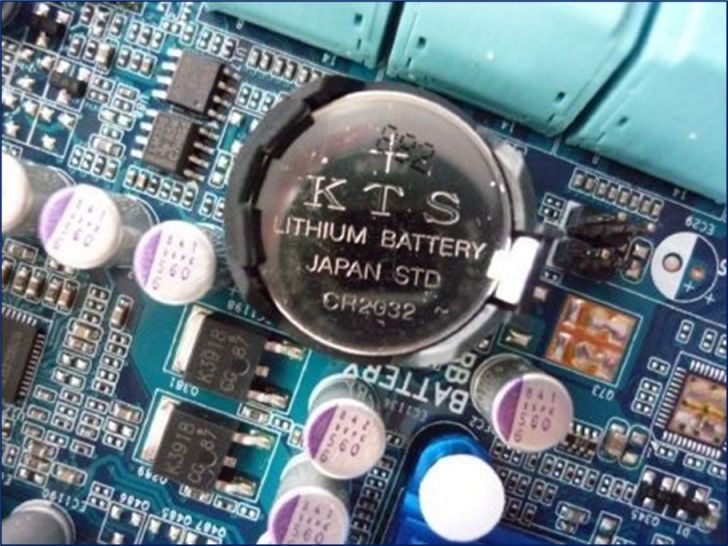
CMOS battery
– The CMOS battery supplies power to the RAM CMOS.
– Specifications:
- Color
- Shape
- Type of battery
- Place of production
4. Requirement of practice
- Every student will receive practical tools.
- Disassemble and assemble the Desktop computer step by step and follow the regulations.
- Identify components of the motherboard.
- Observe and record the specifications of the components of the motherboard.
- Complete the practice sheet for lesson 05.
- You are required to take pictures and record videos for documentation.
5. Practice sheet
Each student downloads the practice sheet here, photo it and bring it with you when you practice.