In this article, we will learn how to use the if…else structure in Python. The if…else statement is used to execute code if a specific condition is met. It allows us to make a decision in the code flow. The logic of the branching control structure if…else in Python is similar to other languages like C++, Java,…
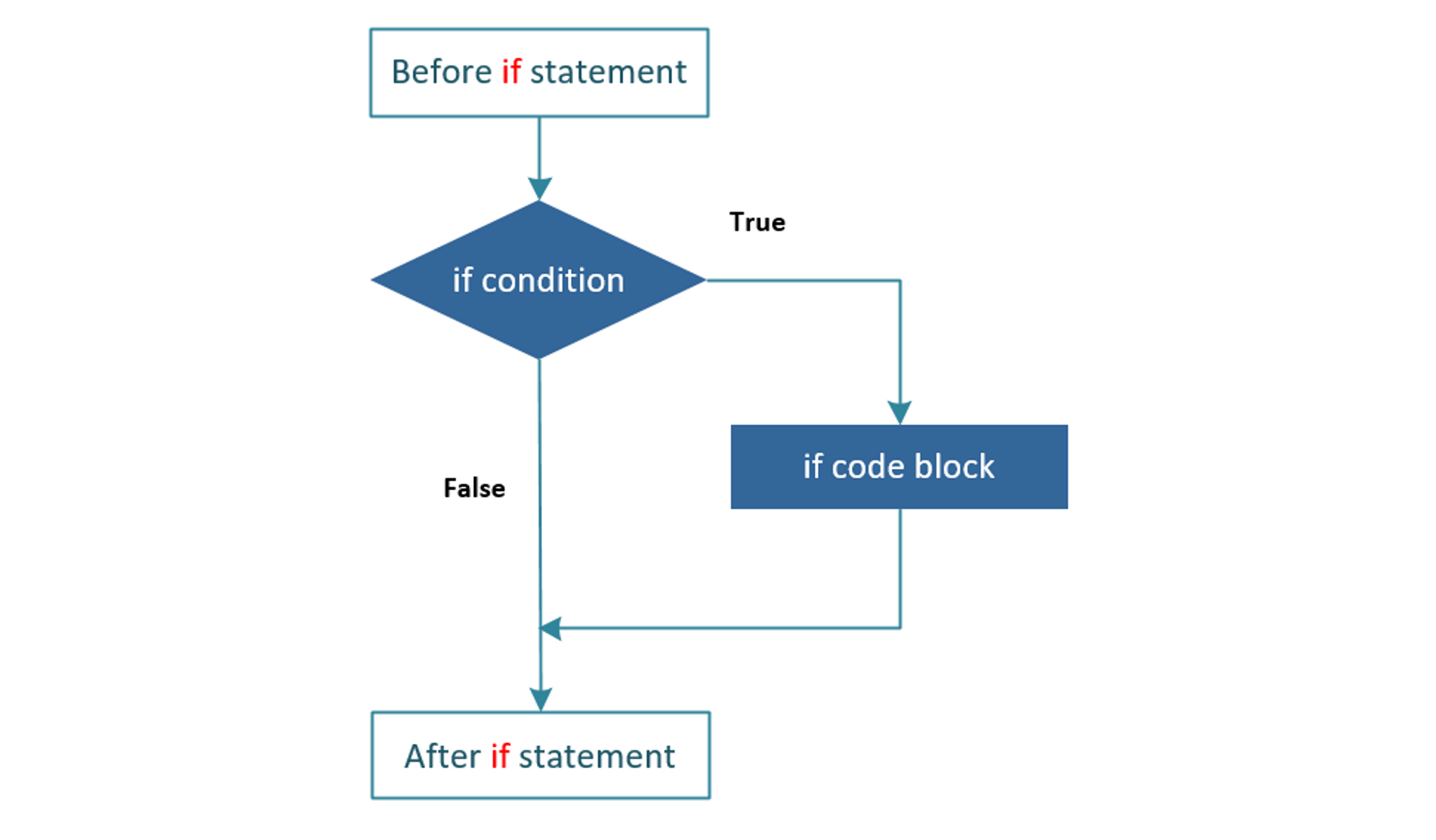
1. If statement in Python
The syntax of the if statement in Python:
if condition:
#statement(s)If condition is True, then the statements in the body of the if statement will be executed. After condition is the colon (:) and the body of the if starts with indentation.
Note: Python’s compiler will understand any condition value different from 0 as True. While None or 0 will be False.
Example:
a = 5
if a>1:
print("a > 1:", True)
a = 5
if a:
print("a:", True)
a = '/'
if a:
print("a = '/':", True)
a = 5
# False, not print True
if a>7:
print("a > 7:", True)
a = 0
# False, not print True
if a:
print("a:", True)
a = None
# False, not print True
if a:
print("a:", True)Result
a > 1: True
a: True
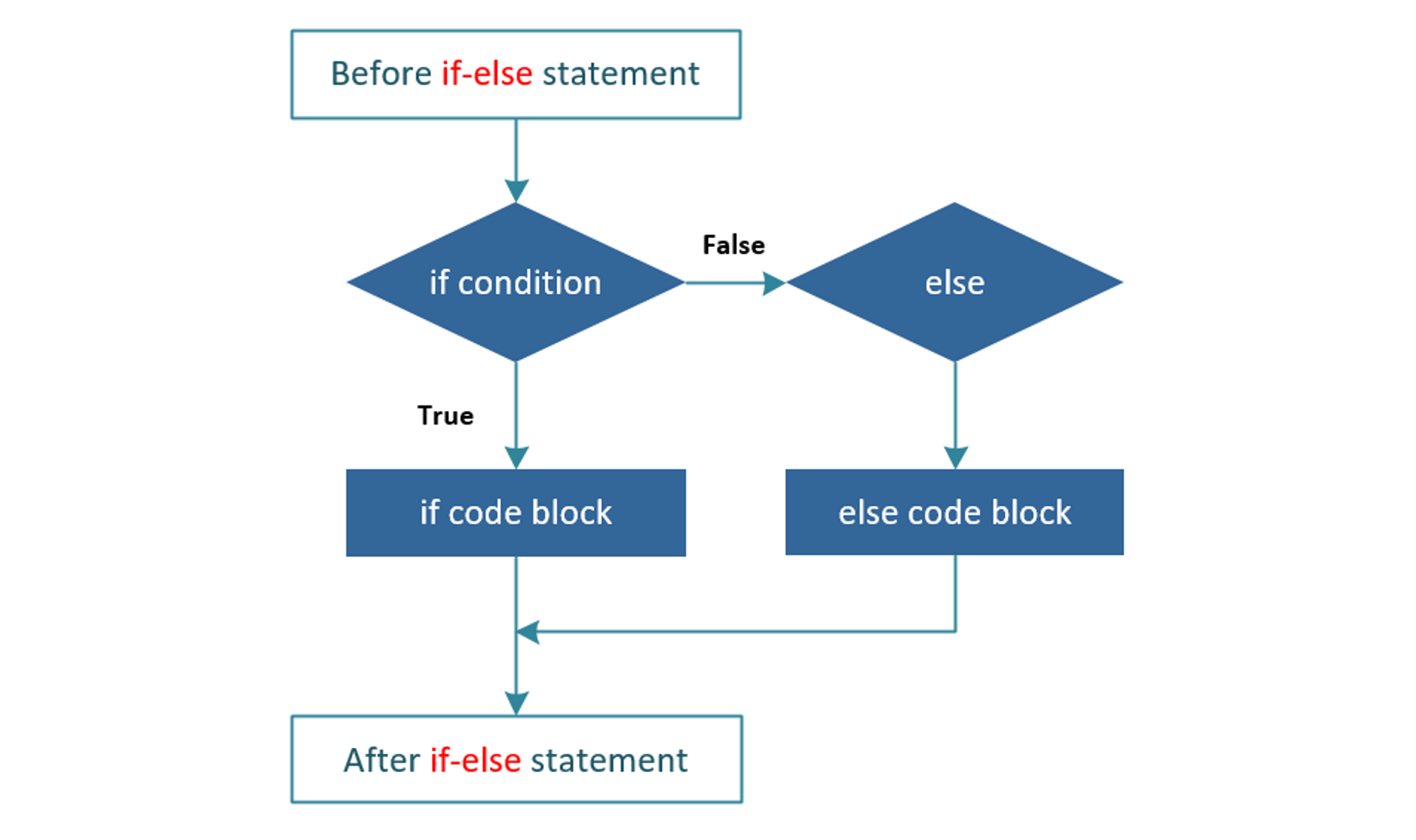
a = '/': True2. If…else statement in Python
The syntax of the if…else statement in Python:
if condition:
#Body of if
else:
#Body of elseIf condition is True, then the statements in the body of the if statement will be executed. Otherwise, if condition is False, the statements in the body of the else statement will be executed.
Example:
num = 3
if num >= 0:
print("num is greater than 0 or equal to 0")
else:
print("num is smaller than 0")
num = -1
if num >= 0:
print("num is greater than 0 or equal to 0")
else:
print("num is smaller than 0")Result
num is greater than 0 or equal to 0
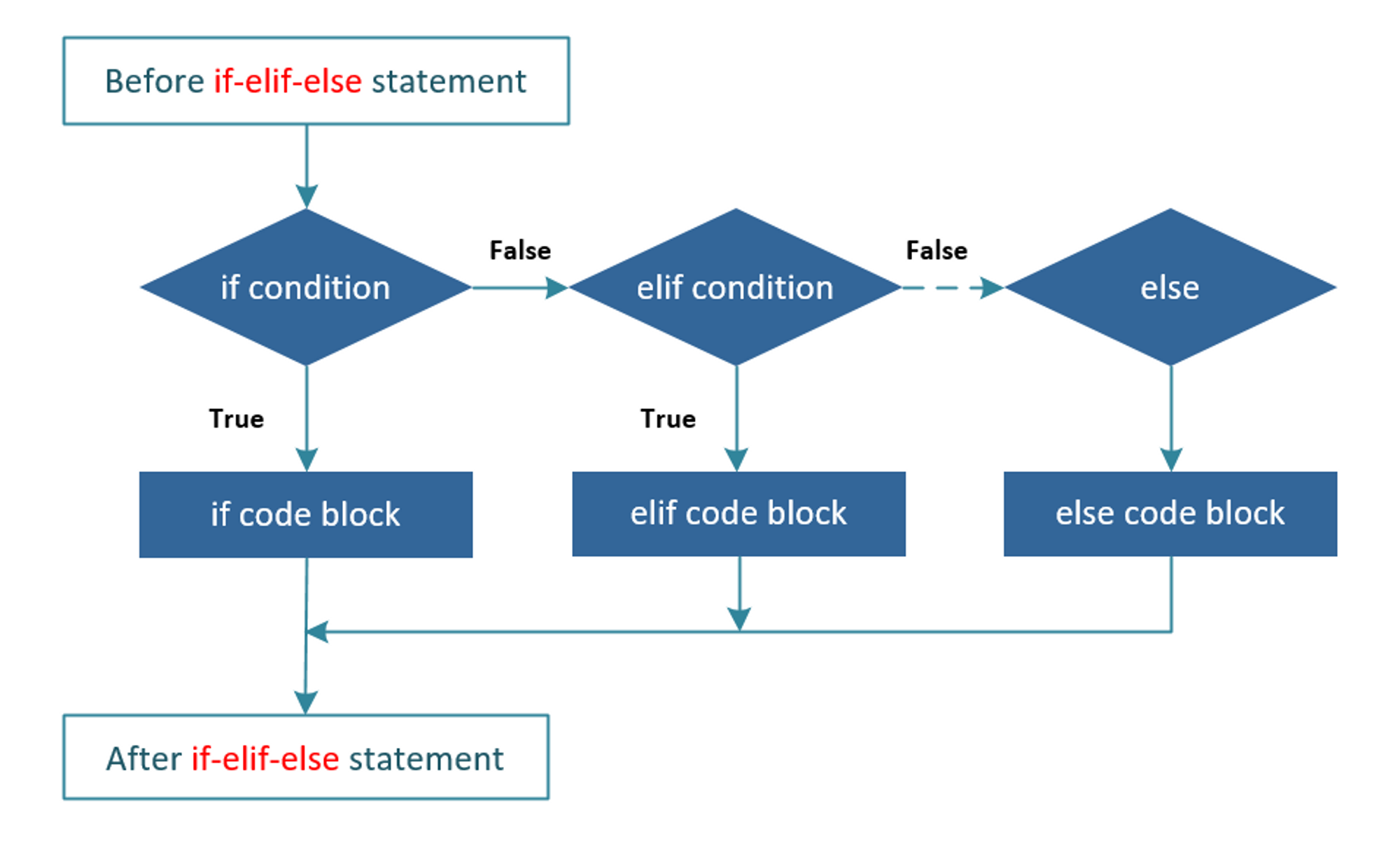
num is smaller than 03. If…elif…else statement in Python
If there are multiple conditions to compare and choose, we can use the if…elif…else statement. The syntax of the if…elif…else statement in Python:
if condition1:
#Body of if
elif condition2:
#Body of elif
else:
#Body of elseIn case of condition1 is True, the body of the if will executed. However, if condition1 is False, we move to condition2. If condition2 is True, it will execute elif statement. On the other hand, the else statement will be executed.
Example:
num = 0
if num > 0:
print("num is greater than 0")
elif num == 0:
print("num is equal to 0")
else:
print("num is smaller than 0")Result
num is equal to 0In case there are more conditions, we can use more elif. Example:
mark = 7.5
if mark >= 9:
print("excellent")
elif mark >= 8 and mark < 9:
print("very good")
elif mark >= 6.5 and mark < 8:
print("good")
elif mark >= 5 and mark < 6.5:
print("average")
elif mark >= 3.5 and mark < 5:
print("weak")
else:
print("poor")Result
good4. Nested if statements in Python
If statements can be in another if statement. This is called a nested if statement. Example:
price = 50
quantity = 5
amount = price*quantity
if amount > 100:
if amount > 500:
print("Amount is greater than 500")
else:
if amount < 500 and amount > 400:
print("Amount is")
elif amount < 500 and amount > 300:
print("Amount is between 300 and 500")
else:
print("Amount is between 200 and 500")
elif amount == 100:
print("Amount is 100")
else:
print("Amount is less than 100")Result
Amount is between 200 and 5005. Shortened if statement in Python
We can write a shortened if statement in 1 line with the following syntax:
if condition: statementExample:
i = 15
if i % 3 == 0 : print(i,"is divisible by 3.")Result
15 is divisible by 3.We can write a shortened if…else statement in 1 line with the following syntax:
statement_when_True if condition else statement_when_FalseExample:
i = 16
print(i,"is divisible by 3.") if i % 3 == 0 else print(i,"is not divisible by 3.")Result
16 is not divisible by 3.Try to master the if…else branching control structure because you will use it a lot in your programs.